
Adoption of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) in Asia-Pacific Health Agencies
27 may 2025

Author: Anjali Malan
Summary: Advances in technology have transformed information systems into inter-organizational systems (IOS), with Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) being a key component. EDI facilitates the exchange of standardized documents and data between organizations, improving efficiency, accuracy, and cost reduction. Countries like Australia, Japan, and Singapore are leading EDI adoption in their healthcare systems. However, challenges like lack of standardized regulations, initial costs, cybersecurity concerns, and high implementation costs persist. Despite these obstacles, with collaboration between governments, healthcare providers, and technology companies, EDI’s potential to transform healthcare is promising.
Advances in computer and communications technology have expanded the traditional role of information systems (IS) from the creation, storage, transformation, and transmission of information within an organization (intra-organizational systems) to the establishment of inter-organizational systems (IOS) that exchange or share information among organizations. According to Sanchez and Perez, electronic data interchange (EDI) is a class of IOS. There are various definitions of EDI. Alam et al. referred to EDI as the exchange of business information from one organization’s application to the computer application of a trading partner. Chang et al. described EDI as the exchange of information through standard electronic formats with communication protocols to exchange business documents among trading partners. Ngai and Gunasekaran stated that EDI is an interorganizational and intraorganizational, computer-to-computer exchange of business documentation in a structured, computer-processable data format in a timely manner. The distinguishing feature between EDI and other e-commerce forms is that EDI data are in a structured format and in a timely manner. The EDI data are preformatted and are based on standards deemed acceptable to all trading partners’ electronic protocols.
THE IMPORTANCE OF EDI IN HEALTHCARE:
Electronic Data Interchange simplifies sharing patient information, medical records, and billing documents among healthcare providers, insurance companies, and government health agencies. By replacing paper-based communication with electronic transactions, EDI reduces the risk of errors, speeds up data processing, and ensures the secure exchange of sensitive health information.
In the Asia-Pacific region, where healthcare systems vary significantly from one country to another, EDI offers a standardized approach to data management, making cross-border collaborations and information sharing more efficient.

The transformational benefits of EDI in healthcare
EDI FACILITATES:
- Increased Efficiency and Expedited Speed: Gone are the days of manual claims processing with delays and redundancies and the need for vast numbers of human resources. EDI has automated these cumbersome processes, increased worker productivity, helped expedite claim resolution, and offered the ability to channel resources effectively.
- Cost Reduction: The economic merits of EDI transcend mere paperwork reductions. The savings stack up significantly from diminished errors, leading to fewer reprocessed claims to less staff and staff focused on value-driven tasks.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: The global push for EDI arises from more government regulation and reimbursement reporting requirements, along with the recognized benefits and subsequent standards set by governments and industry bodies. Adhering to these standards equates to smoother operations and streamlined data exchanges.
- Improved Accuracy and Minimized Errors: By minimizing human intervention, errors are reduced. EDI, with its standardized formats and validations, ensures precise data exchanges, which enhances accuracy overall.
- Advanced Data Analysis Capabilities: EDI makes structured data ready for immediate analysis, which enables swift insights into cost patterns, potential fraud, and more. This ultimately benefits patient care and operational efficiencies.
- Interoperability: EDI delivers interoperability by providing a unifying language in an industry with diverse stakeholders. EDI bridges system disparities and ensures consistent and seamless data exchanges.
- Real-time Data Processing: As always, time is money. Market forces demand speed, and EDI delivers real-time claims processing, which enhances cash flow and business transactions.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: The healthcare landscape constantly evolves with new diseases, treatments, and medical knowledge. The ability to add new codes into the EDI system allows healthcare providers and insurers to adapt to these changes quickly.
- Patient-Focused Care: At healthcare’s core lies the patient. EDI facilitates faster data processing, which leads to more insightful data-driven decisions and, ultimately, a higher quality of care.
- Environmental Benefits: Embracing the digital exchange of data results in lesser paper usage, which translates to clear environmental benefits
ADOPTION OF EDI IN ASIA-PACIFIC HEALTH AGENCIES:
The Asia-Pacific region, home to some of the world’s most populous countries, has witnessed a significant transformation in its healthcare sector over the past decade. A pivotal part of this transformation is the adoption of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), a technology that enables the exchange of standardized documents and data between organizations instead of using paper-based methods like fax, mail, or email. In the context of health agencies, EDI plays a crucial role in streamlining operations, including improved accuracy, improved data management, reduced costs, and enhanced security.
Why is EDI being adopted in Asia Pacific countries?
- Industrialization: China and Japan’s industrialization has led to a rise in the demand for EDI solutions.
- Automation: The adoption of automation solutions in industries like manufacturing has led to a surge in demand for EDI.
- Supply chain: EDI is being used to streamline supply chain operations.
CURRENT ADOPTION TRENDS:
Countries like Australia, Japan, and Singapore lead EDI adoption within their healthcare systems. Australia, for example, has integrated EDI into its national healthcare infrastructure, allowing for seamless communication between hospitals, clinics, and insurance providers. In Japan, EDI is used extensively to manage medical billing and patient records, ensuring that healthcare providers can offer timely and accurate care.
ASIA PACIFIC ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI) MARKET OVERVIEW:
The electronic data interchange (EDI) market in the Asia Pacific (APAC) has been analyzed based on historical, current, and future trends in countries across the region. The EDI market players in the region are experiencing significant demand for their solutions and services as the need for EDI is comparatively high across various industries, including retail, IT & telecom, logistics, BFSI, and others. Most of the countries in the region are economically developing, and thus, the investment in advanced technologies has increased, facilitating several growth opportunities to the EDI market players.
China and Japan are the leading countries in the APAC EDI market due to the steep industrialization rise. The rising adoption of high-end automation solutions among various industries in China and Japan has surged the demand for EDI solutions and services. Several industries, such as BFSI, retail, logistics, and IT, are booming in APAC and are also anticipated to continue to climb substantially during 2022–2030, resulting in a rise in the procurement of EDI solutions and services, thereby catalyzing the EDI market. The EDI solution helps the organization to exchange data accurately and securely with their trading partners. They also enable the organization to reduce operational costs and enhance quality.
The electronic invoicing scope in the APAC market is gradually increasing. The lack of government initiatives, standards, tax impediments, regulatory framework, and proper understanding of the system among users are among a few aspects hindering the adoption of EDI solutions. However, the volume of e-invoices exchanged across APAC is increasing from B2C organizations. Thus, it encourages organizations to invest more in “paperless trade,” which further boosts the EDI market growth in APAC.
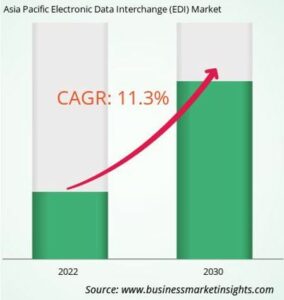
APAC EDI Market
ASIA PACIFIC ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI) MARKET REVENUE AND FORECAST TO 2030 (US$ MILLION):
Asia Pacific Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Market Segmentation
The Asia Pacific electronic data interchange (EDI) market is segmented based on component, Type, Industry, and country.
Based on components, the Asia Pacific electronic data interchange (EDI) market is bifurcated into solutions and services. The solution segment held a larger Asia Pacific electronic data interchange (EDI) market share in 2022.
In terms of Type, the Asia Pacific electronic data interchange (EDI) market is categorized into direct EDI, EDI via AS2, EDI via VAN, mobile EDI, web EDI, EDI outsourcing, and others. The EDI via AS2 segment held the largest Asia Pacific electronic data interchange (EDI) market share in 2022.
By Industry, the Asia Pacific electronic data interchange (EDI) market is segmented into BFSI, retail and consumer goods, healthcare, IT and telecommunication, transportation and logistics, and others. The retail and consumer goods segment held the largest Asia Pacific electronic data interchange (EDI) market share in 2022.
Based on country, the Asia Pacific electronic data interchange (EDI) market is categorized into Australia, China, Japan, India, South Korea, and the Rest of Asia Pacific. China dominated the Asia Pacific electronic data interchange (EDI) market in 2022.
Optum Inc., Pacific Commerce, SPS Commerce Inc., TrueCommerce Inc., Cerner Corp, International Business Machines Corp, Boomi Inc., GoAnywhere MFT, The Descartes Systems Group Inc., and Comarch SA are some of the leading companies in the Asia Pacific electronic data interchange (EDI) market.
ANALYSIS OF MARKET SIZE & TRENDS:
he Asia Pacific Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Software Market will witness market growth of 12.8% CAGR during the forecast period (2024-2031).
The China market dominated the Asia Pacific Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Software Market by Country in 2023 and would continue to be a dominant market till 2031, thereby achieving a market value of $712.6 million by 2031. The Japan market is registering a CAGR of 12.1% during (2024 – 2031). Additionally, The India market would showcase a CAGR of 13.6% during (2024 – 2031).
Analysis of Market 2023-2031
Many industries, including retail, automotive, and healthcare, have adopted EDI as a standardized method for data exchange, making it a common practice across sectors. Industry-wide initiatives promoting EDI adoption have increased participation among suppliers and partners, enhancing collaborative efforts.
Government regulations and incentives have accelerated EDI adoption in healthcare industries, promoting compliance with HIPAA standards and reducing paperwork through electronic documentation.
As the logistics industry expands, the demand for streamlined processes and improved operational efficiency will drive the adoption of EDI software. EDI facilitates seamless electronic communication between businesses, reducing paperwork, minimizing errors, and enhancing overall efficiency in supply chain management. In a rapidly growing logistics environment, companies will likely seek advanced EDI solutions to support real-time data exchange, improve inventory management, and optimize order fulfillment processes.
Based on Deployment, the market is segmented into Cloud and On-Premises. Based on Industry, the market is segmented into Retail, Healthcare, Automotive, High-Tech/Manufacturing, Financial Services, Logistics, and Other Industries. Based on Type, the market is segmented into Outsourcing, In-house, and Hybrid. Based on countries, the market is segmented into China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Malaysia, and Rest of Asia Pacific.
According to our new research study on “Asia Pacific Healthcare EDI Market Forecast to 2028 – COVID-19 Impact and Global Analysis – by Technology, Application, End User, and Region,” the Asia Pacific healthcare EDI market is expected to grow from US$ 409.35 million in 2022 to US$ 1,208.20 million by 2030; it is estimated to register a CAGR of 14.5% during the forecast period. The growing need for seamless processing of healthcare claims and administrative transactions and the increasing adoption of healthcare EDI platforms in supply chain tracking are the major factors contributing to the market growth.
INCREASING ADOPTION OF HEALTHCARE EDI PLATFORM IN SUPPLY CHAIN TRACKING:
Hospitals face unprecedented pressure to improve the traditional supply chain process, ultimately reducing cost, quality, and customer experience. Three of the most common issues in the healthcare industry’s supply chain are inadequate inventory management, manual data entry errors, and regulatory compliance and reporting. For example, when medical product suppliers do not utilize healthcare EDI, the healthcare organizations need help in delivering quality patient care, and suppliers lose competitive advantage over other suppliers, spoiling business relationships. Therefore, incorporating healthcare EDI in the supply chain offers the best solution to mitigate supply chain errors. For example, healthcare EDI enables real-time communication of maintaining inventory levels in the medical device industry.
EDI also provides more accurate demand forecasts and allows healthcare suppliers to maintain inventories with the products their customers need and ultimately optimize inventory levels. Further, EDI reduces manual data entry errors across the supply chain by automating the exchange of information between trading partners and ensuring the accurate and consistent transmission of data across the supply chain, keeping the order fulfillment process streamlined and accurate. The EDI also manages regulatory compliance and reporting across the supply chain. For example, by properly utilizing the healthcare EDI transactions, healthcare product suppliers can take advantage of the automatic generation and exchange of necessary documents related to regulatory compliance and build an electronic audit record demonstrating compliance.
Furthermore, medical product suppliers can take advantage of cloud-based EDI managed services, EDI value-added networks (VANs), and EDI training and consulting services. “Cloud-Based EDI Managed Services” and “EDI Value-Added Network (VAN)” solutions offered by the GraceBlood LLC. company are among such examples. EDI Managed Services automates the process in order to help the business grow in less time. Cloud-based EDI-managed services utilize fewer resources and help meet the ever-changing demand of the supply chain, resulting in growing business more than ever. Additionally, EDI VAN has proven the scalability and service levels through features such as Open Web Services, APIs, and Fully Cloud-Enabled Architecture with minimum supply chain-associated cost. Therefore, the utilization of healthcare EDI in supply chain processes ultimately drives market growth through limited resource utilization and cost.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES:
Outsourcing Healthcare EDI Services
EDI implementation through third-party/outsourced solutions saves time, internal resources, and implementation costs. For example, EDI, through outsourced solutions, provides a wide range of pricing models to the organization, with the majority being subscription models. Therefore, the majority of the providers are charged based on the volume of data transmitted through EDI networks.
Although an in-house solution provides the advantage of complete internal management, security, and control, it incurs a high cost of EDI implementation. Therefore, a majority of organizations choose to utilize a third-party EDI provider that addresses all the electronic data interchange within the departments with less cost of implementation. A minimal EDI cost through third-party providers helps small and medium-sized businesses manage EDI implementation costs and launch in-house EDI infrastructure with a minimum budget. Therefore, the calculation of EDI implementation cost is critical to determine the actual financial and business benefits to the organization. If any organization fails to calculate the finance related to healthcare EDI cost implementation, it significantly affects the revenue side of the organization. Therefore, utilizing outsourcing EDI services provides a lucrative opportunity for market growth.
Siemens Healthineers AG, GE Healthcare Technologies Inc., Wipro Ltd., athenahealth Inc., PNORS Technology Group Pty Ltd, International Business Machines Corp, Cognizant Technology Solutions Corp, Veradigm Inc, Oracle Corp, McKesson Corp, and Optum Inc are among the leading companies operating in the Asia Pacific healthcare EDI market.
The “Asia Pacific Healthcare EDI Market” is segmented on the basis of component, delivery mode, application, end user, and region.
In Jun-2023, Cognizant announced an expansion of their long-standing healthcare collaboration with Microsoft, to give healthcare payers and providers easy access to cutting-edge technology solutions, streamlined claims management, and improved interoperability to optimize business operations and deliver better patient and member experiences.
THE FUTURE OF EDI IN ASIA-PACIFIC:
Looking ahead, the future of EDI in Asia-Pacific health agencies appears promising. With the increasing focus on digital health solutions, governments, and private sectors are investing heavily in technology to improve healthcare delivery. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the shift towards digital solutions, highlighting the need for efficient data exchange systems like EDI.
As more countries in the region recognize the benefits of EDI, we can expect to see a broader adoption of this technology. Collaboration between governments, healthcare providers, and technology companies will be essential to overcome the challenges and maximize the potential of EDI in improving healthcare outcomes.
EMPOWERING A HEALTHIER FUTURE THROUGH DIGITAL INNOVATION:
In conclusion, the ascent of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) in healthcare, energized by the Affordable Care Act (ACA) or “Obamacare”, marks a transformative era of enhanced efficiency and patient-centric care. EDI has become crucial in streamlining healthcare operations, ensuring compliance, and fostering transparency, driving a significant shift towards optimized care delivery. Solutions like PilotFish are at the forefront, providing a robust, intuitive integration engine IDE (eiConsole) and platform (eiPlatform) that adapt and scale with the Industry’s evolution. As a result, EDI’s strategic implementation is essential for a connected, efficient, and forward-looking healthcare ecosystem.
CHALLENGES IN IMPLEMENTATION:
Despite the advantages, the adoption of EDI in Asia-Pacific health agencies faces several challenges. One major hurdle is the lack of standardized regulations across the region. Different countries have varying levels of technological infrastructure and regulatory frameworks, making it difficult to implement a uniform EDI system.
Additionally, the initial cost of setting up EDI systems can be prohibitive for smaller healthcare providers, particularly in developing countries. There is also a need for ongoing training and support to ensure that healthcare staff are proficient in using these systems effectively.
- Cybersecurity Concerns:
Cybersecurity threats remain a major barrier to EDI adoption. In 2023, the global cost of cybercrime reached USD 8 trillion, as reported by the World Bank, with industries like healthcare and retail being prime targets. EDI systems, which often involve the exchange of sensitive business data, are increasingly susceptible to ransomware attacks, phishing, and data breaches. The high cost of implementing advanced cybersecurity measures, such as encryption and secure networks, discourages smaller enterprises from adopting EDI despite its operational benefits.
- High Costs of Implementation:
Implementing an EDI system, especially for SMEs, involves substantial initial investment. A 2024 report by the World Bank states that setting up a fully functional EDI system with integration, training, and security measures can cost upwards of USD 500,000 for large organizations. This cost is higher in developing economies where infrastructure limitations add to the complexity. The IMF reports that SMEs, particularly in Latin America, struggle with the high costs of integrating EDI, leading to slow adoption in the region
CONCLUSION:
In conclusion, while the adoption of EDI in Asia-Pacific health agencies is still in its early stages, the technology holds immense potential to transform the healthcare landscape in the region. By addressing the existing challenges and fostering collaboration, Asia-Pacific countries can harness the power of EDI to enhance patient care and operational efficiency.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.kenresearch.com/industry-reports/global-electronic-data-interchange-market.
- https://appinventiv.com/blog/edi-in-healthcare/
- https://www.precedenceresearch.com/healthcare-electronic-data-interchange-market
- https://healthcare.pilotfishtechnology.com/healthcare-edi-adoption-aca-pilotfish-integration/#:~:text=Cost%20Reduction:%20The%20economic%20merits%20of%20EDI,push%20for%20EDI%20arises%20from%20more%20government
- https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/reports/asia-pacific-electronic-data-interchange-edi-market
- Asia Pacific Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Software Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Deployment (Cloud and On-Premises) By Industry, By Type (Outsourcing, In-house, and Hybrid), By Country and Growth Forecast, 2024 – 2031 Report Id: KBV-25224Publication Date: October-2024Number of Pages: 121
- 2021b, Demand & Impacts on Tech & Digital Skills, August.
- Electronic data interchange adoption from technological, organisational and environmental perspectives Article in International Journal of Business Information Systems · January 2015
Register to our news and events
Go to our Events to register
Go to our News to get insights
